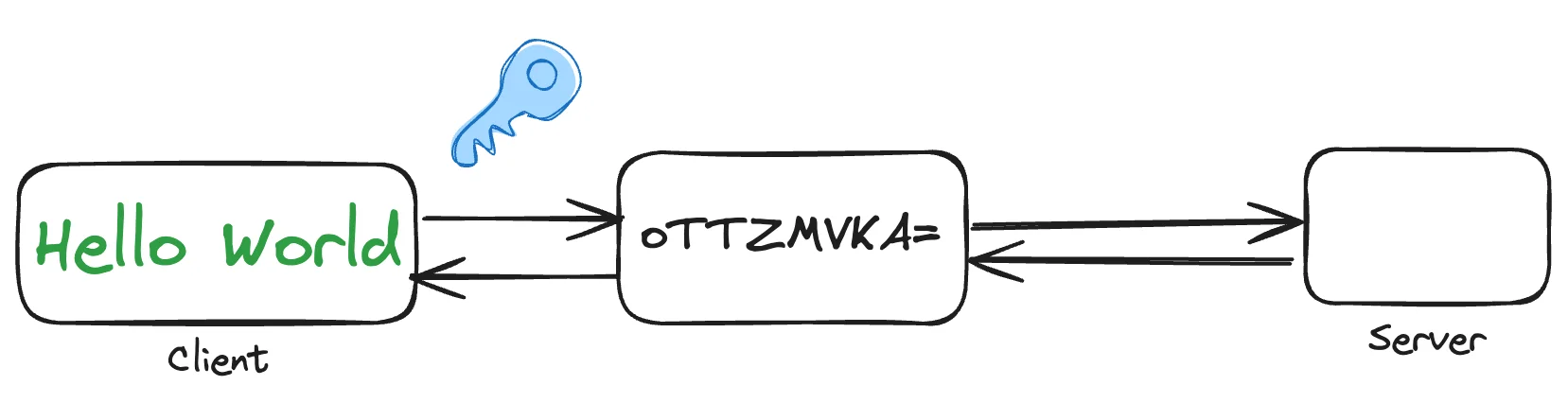
How LogSeam Searches 500 Million Logs per second
How LogSeam Searches 500 Million Logs per second
LogSeam transforms log management with Tigris, achieving massive cost savings and performance improvements in their security data lake architecture.
· 6 min read