Architecture
Tigris is designed with a reliable and scalable architecture at its core, allowing for building a globally distributed system that can be readily scaled to accommodate evolving needs.
One of the key design decisions is to have a composable architecture that allows building a complex distributed system by combining smaller, independent building blocks or services. Each component within Tigris is designed to serve a specific function and can be scaled independently.
A Tigris object store deployment consists of API gateways, a cache layer, a data distribution and replication framework, and data and metadata storage services.
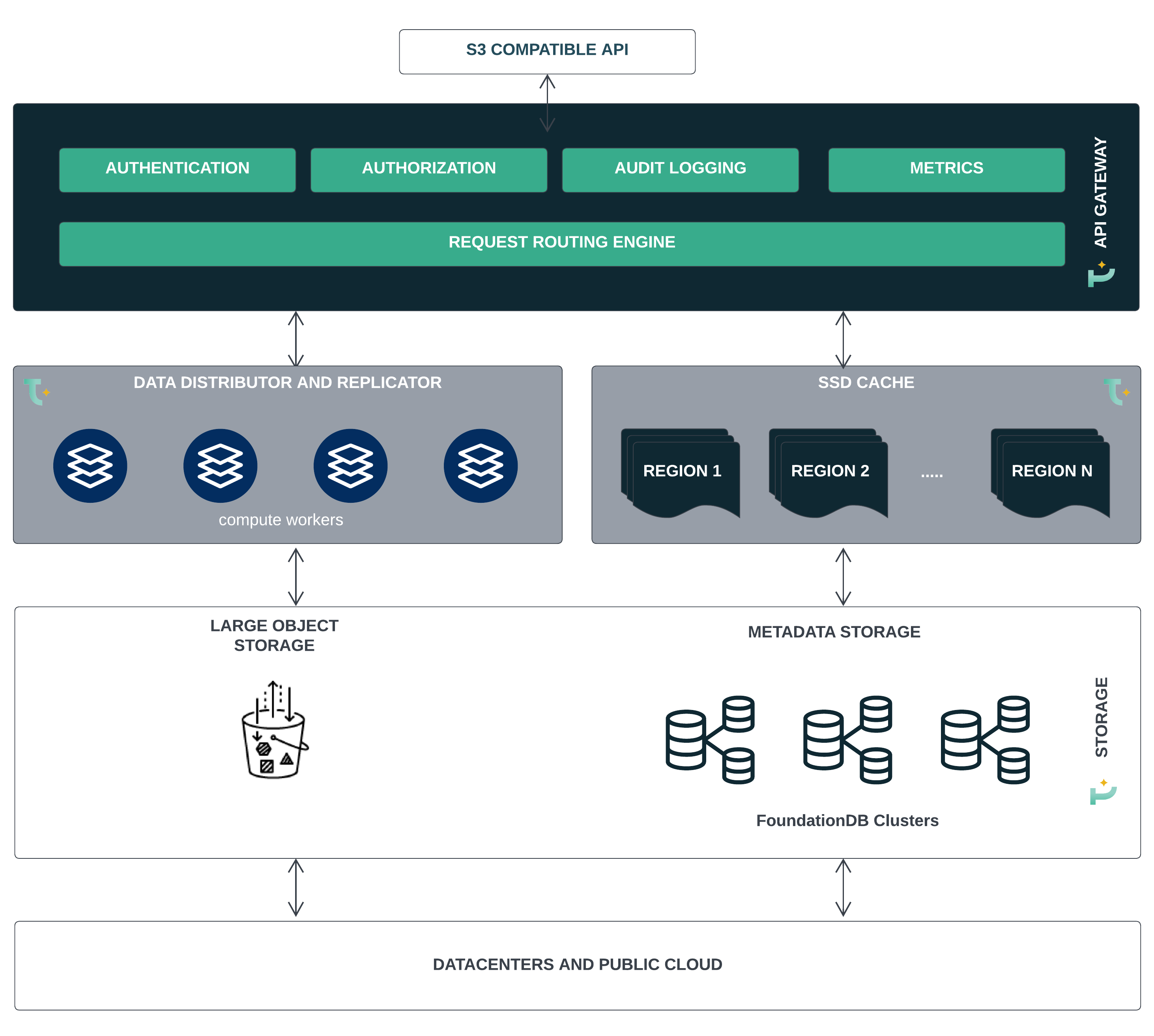
The subsequent section describes each of the major components of Tigris in more detail.
API Gateway
API Gateway layer is the first layer of interaction between users' applications and the Tigris object storage service. The gateway layer conforms to S3 APIs, understands the semantics of the request, and is responsible for authentication, authorization, request processing, and routing.
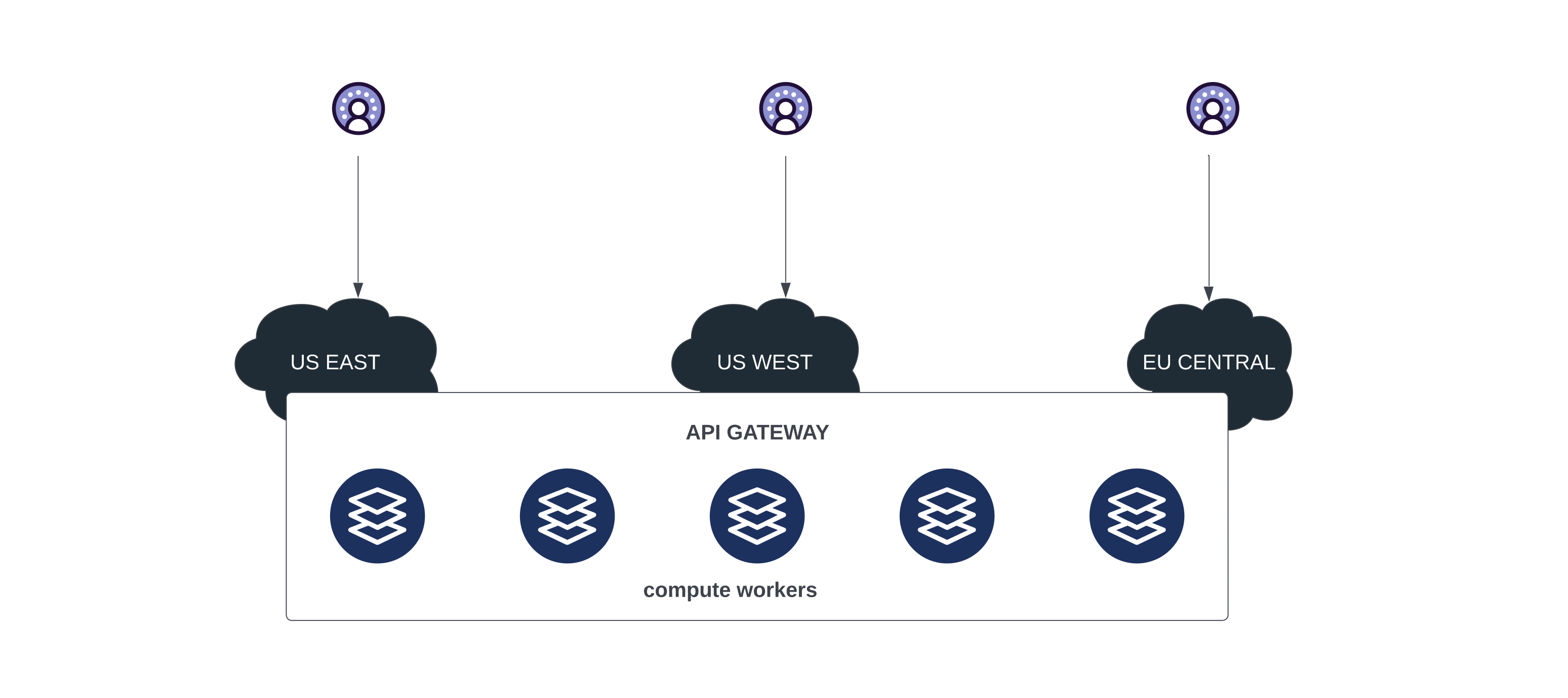
The API gateway is deployed across multiple regions as stateless compute workers and handles the requests close to the user.
Distributed Caching
Tigris transparently caches the data close to the user to provide low-latency access. Caching is provided through a distributed global caching layer with cache nodes deployed in all regions where gateways are deployed. This ensures that user requests can be served from the region closest to the user.
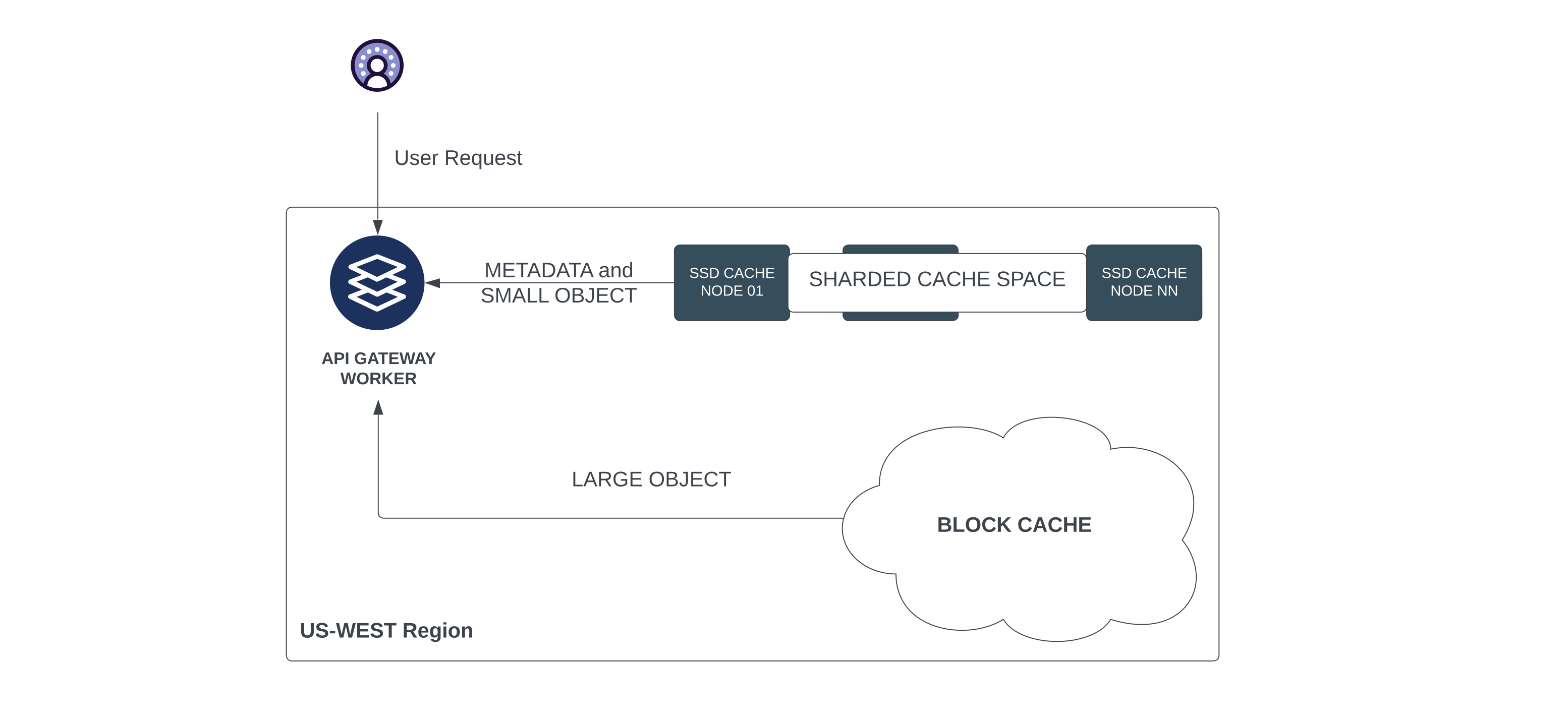
The figure above shows a cache deployment in one of the regions (US-WEST). Similar deployments exist in all the regions.
Tigris supports two caching strategies:
- Cache on Read (default) Depending on the access pattern of objects, the objects get cached.
- Cache on Write (configurable) This is eager caching, where the cache is populated when the object is written. Cache-on-Write can be configured on a per-bucket basis. We have found Cache-on-Read to be sufficient for most of the use cases and the most cost-effective, but Cache-on-Write is available for use cases that need it.
Metadata Storage
We have designed the object storage service such that metadata storage is a separate layer that is deployed separately from object storage. We have also designed the metadata storage to be transactional so that we can provide strong consistency guarantees and powerful semantics such as Compare-And-Set, Transactions over objects, and rich querying functionality, none of which is provided by S3.
Metadata includes metadata about the objects (such as object location, user-supplied metadata, etc), buckets information, users and organization information, access policies, and permissions.
FoundationDB
All of this data is stored in FoundationDB. FoundationDB is an ordered, distributed, transactional, key-value store that provides support for multi-key strictly serializable transactions across the entire keyspace. FoundationDB is used by Apple, Snowflake, and countless others as a stand-alone, production-ready distributed key-value store with interactive transactions. It provides the same consistency guarantees as Spanner (strict serializability), and has an amazing correctness story through simulation testing.
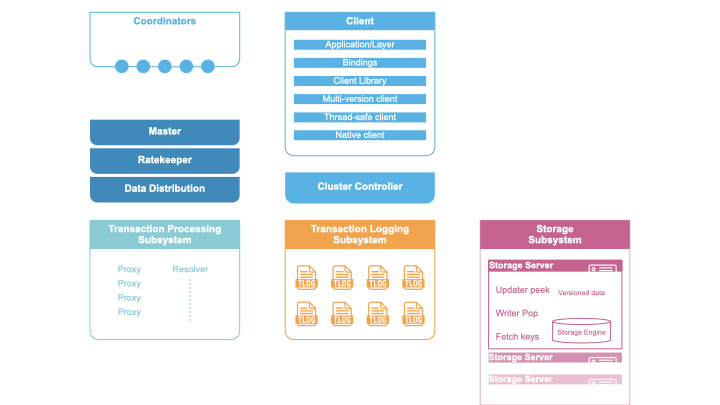
(reference: https://apple.github.io/foundationdb/architecture.html)
FoundationDB provides us the ability to store large amounts of metadata while ensuring high availability, high degree of consistency, and durability.
FoundationDB inherently supports sharding through the lexicographical sorting of keys. We construct a unique object key and use that for sharding, with each object being mapped to a logical shard and subsequently to a physical storage node.
Multi-cluster Redundancy and Replication
To safeguard against region-wide failures, we deploy and run multiple FoundationDB clusters for increased redundancy and failure protection. The data is replicated between the FoundationDB clusters through a replication service that we have developed.
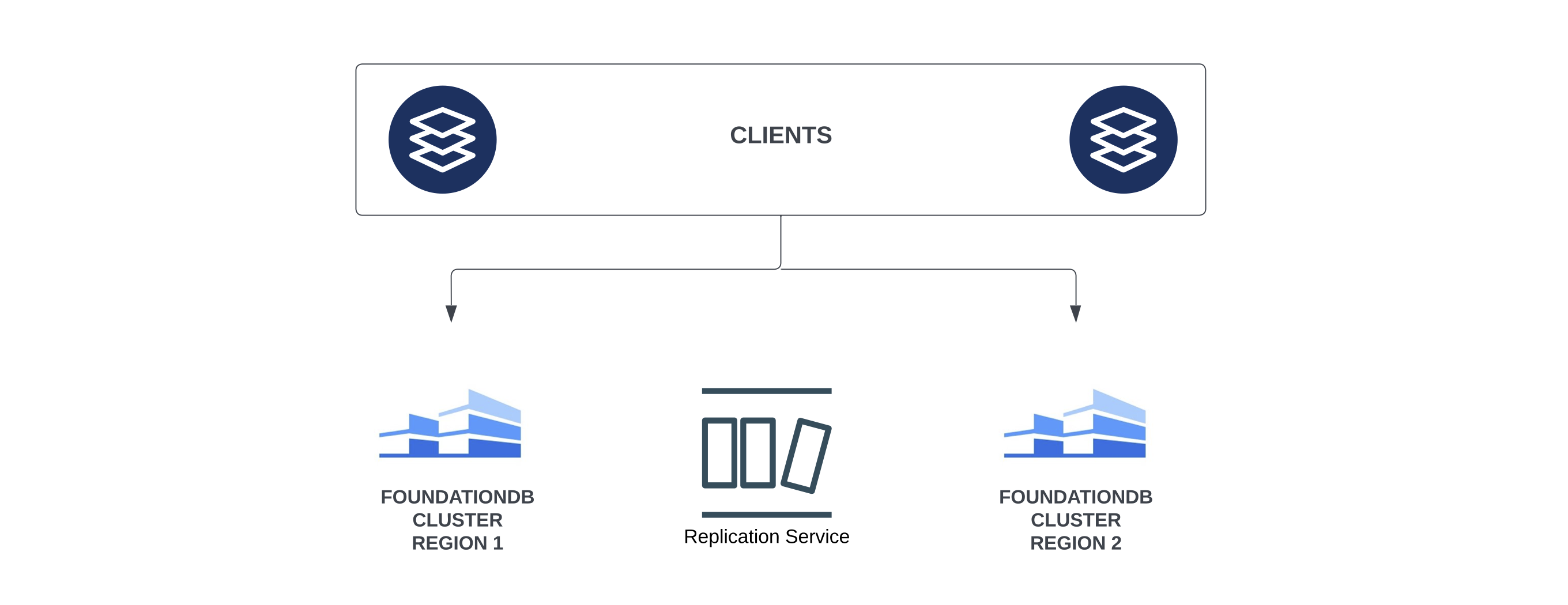
Data Storage
Long-term storage of objects is done on block stores. Before storing an object, its metadata is extracted and stored in Metadata Storage, while its content is stored in the block store.
When choosing the block store for storing the object, the one closest to the user is chosen. This allows us to provide low-latency reads and writes.
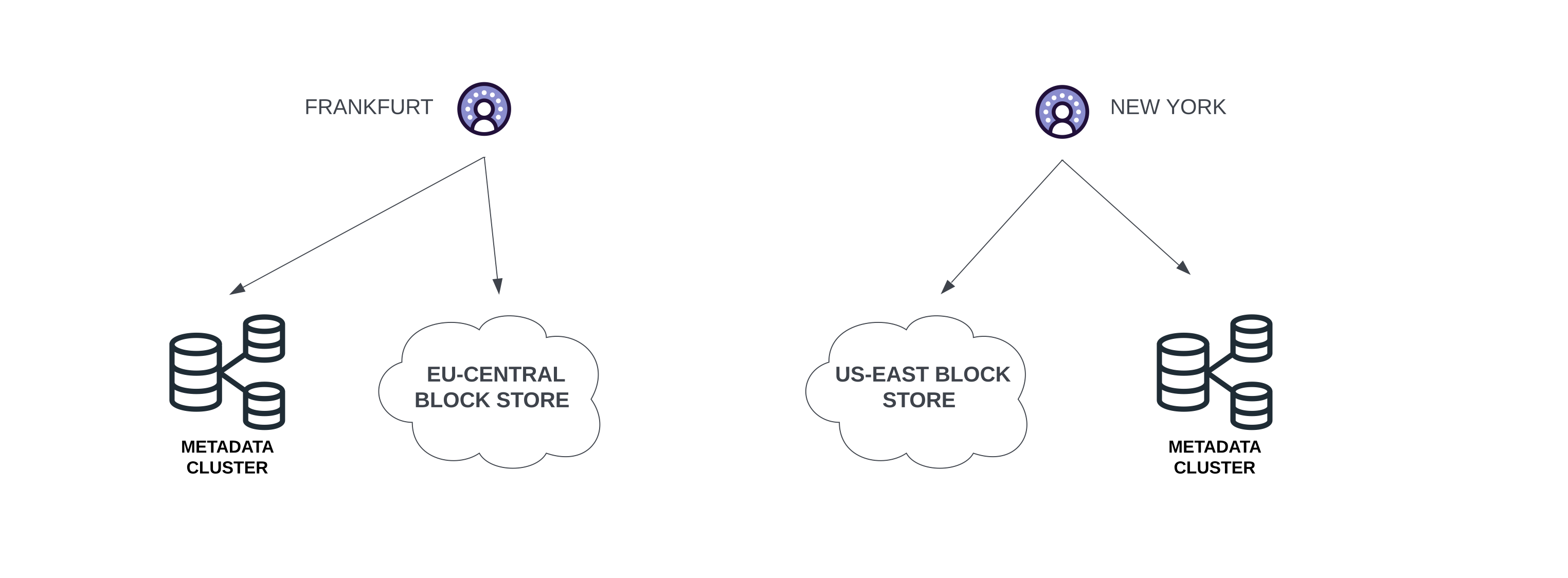
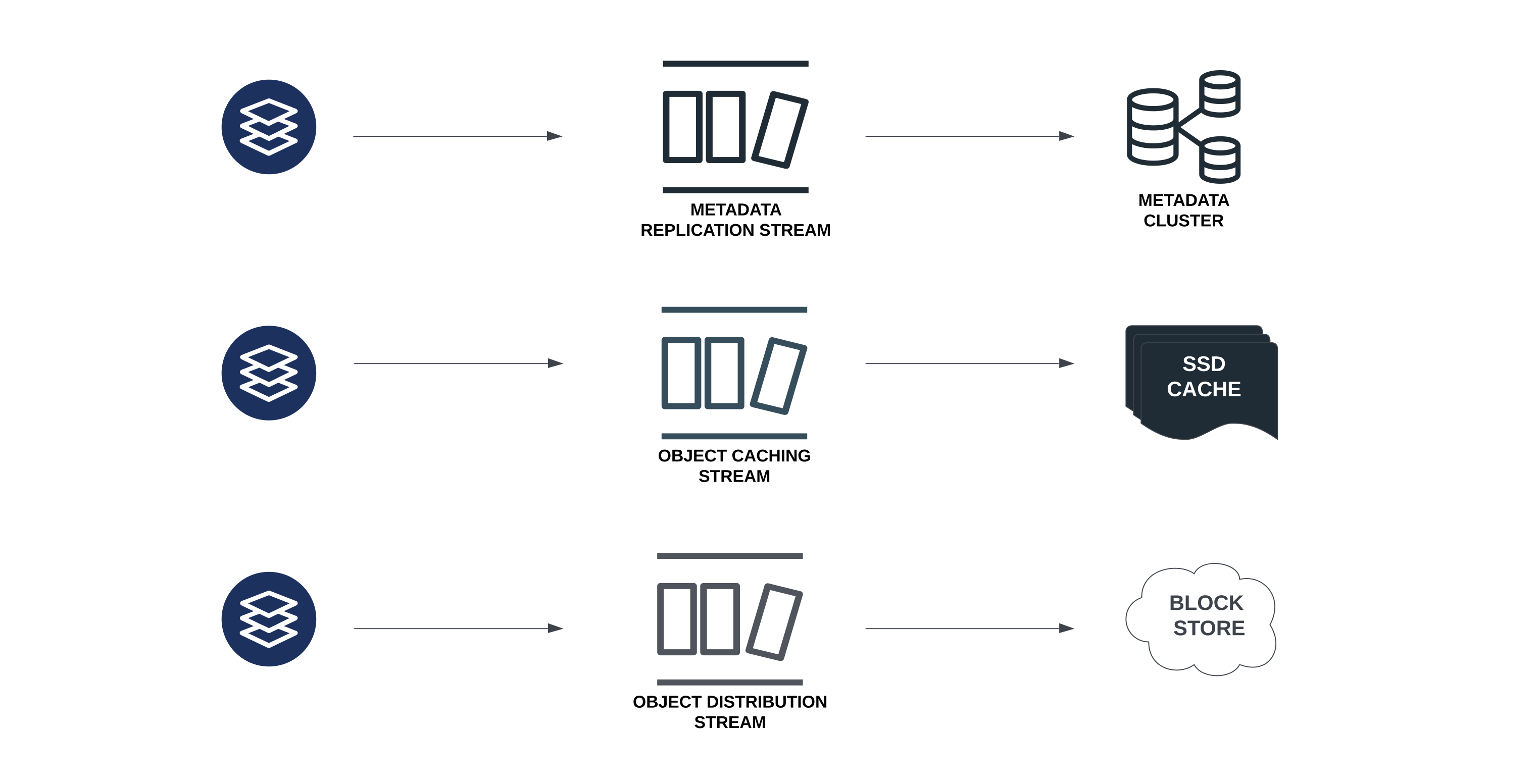
Data Distributor and Replicator
During the lifetime of storage of an object, the object may need to be distributed to multiple locations either for caching, redundancy purposes or because of a change in access pattern. Hence, the data distribution and replication framework forms a key part of our system.
The framework design is centered around a distributed persistent queue backed by FoundationDB. It is an adaptation of Apple's QuiCK paper.
Some of the responsibilities of the data distribution framework are:
- Replication between FoundationDB clusters
- Caching objects in multiple geographical locations
- Invalidating caches automatically on writes
- Redundant storage of objects if requested by the user
- Moving the object from one location to another